Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
dew's CSE Studying
6장 LAB 문제풀이 본문
LAB 1: 단어들을 저장하는 연결리스트
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct {
char name[100];
}element;
typedef struct ListNode {
element data;
struct ListNode* link;
}ListNode;
//오류처리함수
void error(char* message)
{
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", message);
exit(1);
}
//INSERT_FIRST
ListNode* insert_first(ListNode* head, element value)
{
ListNode* p = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
p->data = value;
p->link = head;
head = p;
return head;
}
//print_list(출력형태 %s로 변경)
void print_list(ListNode* head)
{
for (ListNode* p = head; p != NULL; p = p->link)
printf("%s->", p->data.name);
printf("NULL \n");
}
//테스트 프로그램
int main(void)
{
ListNode* head = NULL;
element data;
strcpy(data.name, "APPLE");
head = insert_first(head, data);
print_list(head);
strcpy(data.name, "KIWI");
head = insert_first(head, data);
print_list(head);
strcpy(data.name, "BANANA");
head = insert_first(head, data);
print_list(head);
return 0;
}
LAB 2: 특정한 값을 탐색하는 함수
[코드]
//노드값 탐색 알고리즘
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int element;
typedef struct {
element data;
struct ListNode* link;
}ListNode;
ListNode* insert_first(ListNode* head, element value)
{
ListNode* p = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
p->data = value;
p->link = head;
head = p;
return head;
}
void print_list(ListNode* head)
{
for (ListNode* p = head; p != NULL; p=p->link)
printf("%d->", p->data);
printf("NULL \n");
}
//노드값 탐색함수
ListNode* search_list(ListNode* head, element x)
{
ListNode* p = head; //시작은 헤드포인터가 가리키는 함수
while (p != NULL) { //제일 끝까지
if (p->data == x)return p;
p = p->link; //순서대로 링크를 따라가면서 노드의 저장값과 찾는 값 x를 비교한다
}
return NULL;
}
//테스트프로그램
int main(void)
{
ListNode* head = NULL;
head = insert_first(head, 10);
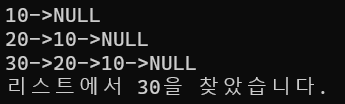
print_list(head);
head = insert_first(head, 20);
print_list(head);
head = insert_first(head, 30);
print_list(head);
if (search_list(head, 30) != NULL)
printf("리스트에서 30을 찾았습니다. \n");
else
printf("리스트에서 30을 찾지 못했습니다. \n");
return 0;
}[실행결과]
LAB 3: 두 개의 리스트를 하나로 합치는 함수 작성
[알고리즘]
두 개의 리스트를 합치려면 첫 번째 리스트의 맨 끝으로 간 다음, 마지막 노드의 링크가 두 번째 리스트의 첫 번째 노드를 가리키도록 변경하면 된다. list1이나 list2가 NULL인 경우를 주의해야 한다!
[코드]
//리스트 합치는 거 concat_list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int element;
typedef struct {
element data;
struct ListNode* link;
}ListNode;
ListNode* insert_first(ListNode* head, element value)
{
ListNode* p = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
p->data = value;
p->link = head;
head = p;
return head;
}
void print_list(ListNode* head)
{
for (ListNode* p = head; p != NULL; p=p->link)
printf("%d->", p->data);
printf("NULL \n");
}
//리스트 연결함수
ListNode* concat_list(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2)
{
if (head1 == NULL)return head2;
else if (head2 == NULL)return head1;
else {
ListNode* p = head1; //시작은 헤드포인터가 가리키는 함수
while (p->link != NULL) //리스트의 끝까지 갈 때까지
p = p->link; //p=p의 링크값
p->link = head2;
return head1;
}
}
//테스트프로그램
int main(void)
{
ListNode* head1 = NULL;
ListNode* head2 = NULL;
head1 = insert_first(head1, 10);
head1 = insert_first(head1, 20);
head1 = insert_first(head1, 30);
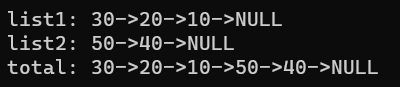
printf("list1: ");
print_list(head1);
head2 = insert_first(head2, 40);
head2 = insert_first(head2, 50);
printf("list2: ");
print_list(head2);
ListNode* total = concat_list(head1, head2);
printf("total: ");
print_list(total);
return 0;
}[실행결과]
LAB 4: 리스트를 역순으로 만드는 연산
[알고리즘]

p=역순으로 만들 리스트
q=현재 역순으로 만들 노드
r=이미 역순으로 변경된 리스트
r->q->p를 차례로 따라간다
[코드]
//노드값 탐색 알고리즘
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int element;
typedef struct {
element data;
struct ListNode* link;
}ListNode;
ListNode* insert_first(ListNode* head, element value)
{
ListNode* p = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
p->data = value;
p->link = head;
head = p;
return head;
}
void print_list(ListNode* head)
{
for (ListNode* p = head; p != NULL; p=p->link)
printf("%d->", p->data);
printf("NULL \n");
}
//역순 연산
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head)
{
//순회포인터로 p,q,r을 사용
ListNode* p, * q, * r;
p = head; //p는 역순으로 만들 리스트
q = NULL; //q는 역순으로 만들 노드
while (p != NULL) {
r = q; //r은 역순으로 된 리스트
//r->q->p를 따라간다
q = p;
p = p->link;
q->link = r; //q의 링크 방향을 바꾼다
}
return q;
}
//테스트프로그램
int main(void)
{
ListNode* head1 = NULL;
ListNode* head2 = NULL;
head1 = insert_first(head1, 10);
head1 = insert_first(head1, 20);
head1 = insert_first(head1, 30);
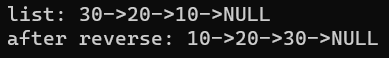
printf("list: ");
print_list(head1);
head2 = reverse(head1);
printf("after reverse: ");
print_list(head2);
return 0;
}[실행결과]
'2-2 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 9.4 히프의 구현(히프트리 전체 함수) (1) | 2023.11.16 |
|---|---|
| 8.10 스레드이진트리 순회 프로그램 (7) | 2023.11.15 |
| 8.4 이진트리의 순회 (2) | 2023.11.15 |
| 4장 연습문제 #10, #11, #12 (3) | 2023.10.21 |
| 4.4 스택의 응용: 괄호 검사 문제 (2) | 2023.10.18 |


